Search
Key Quality Inspection Methods for Rigid-Flex Boards in Manufacturing Processes
- May 28,2025
-
Share
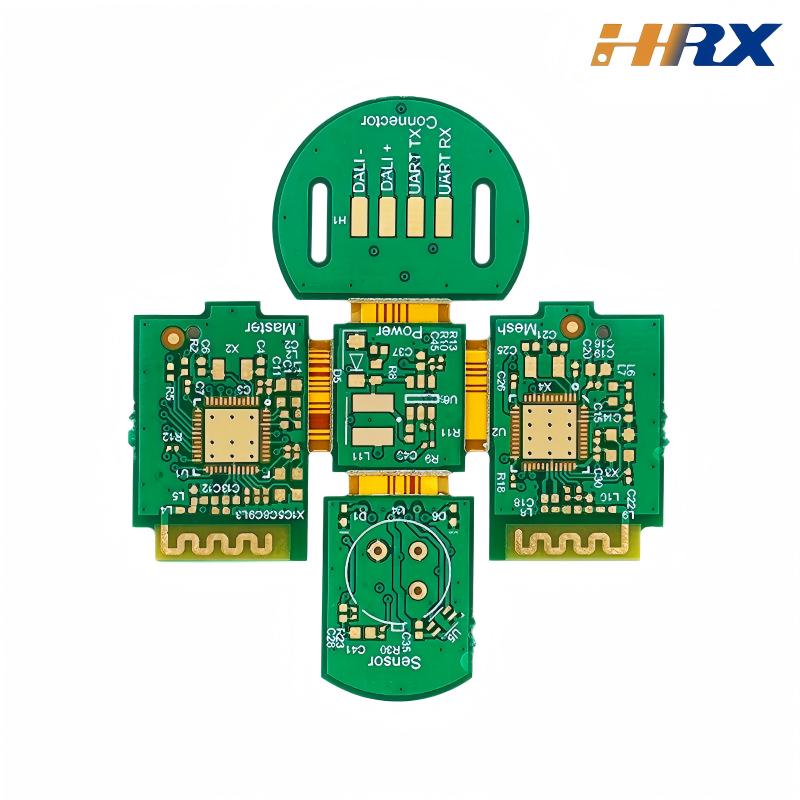
In the production of rigid-flex printed circuit boards (RFPCs), ensuring superior quality requires rigorous inspection at every stage to identify defects and maintain reliability. As a leading global ODM/OEM manufacturer specializing in FPC (flexible printed circuits), PCB (printed circuit boards), and rigid-flex boards, Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics emphasizes that advanced quality inspection methods are critical to meeting industry standards. Below are key techniques and insights to ensure precision and performance in rigid-flex board manufacturing.
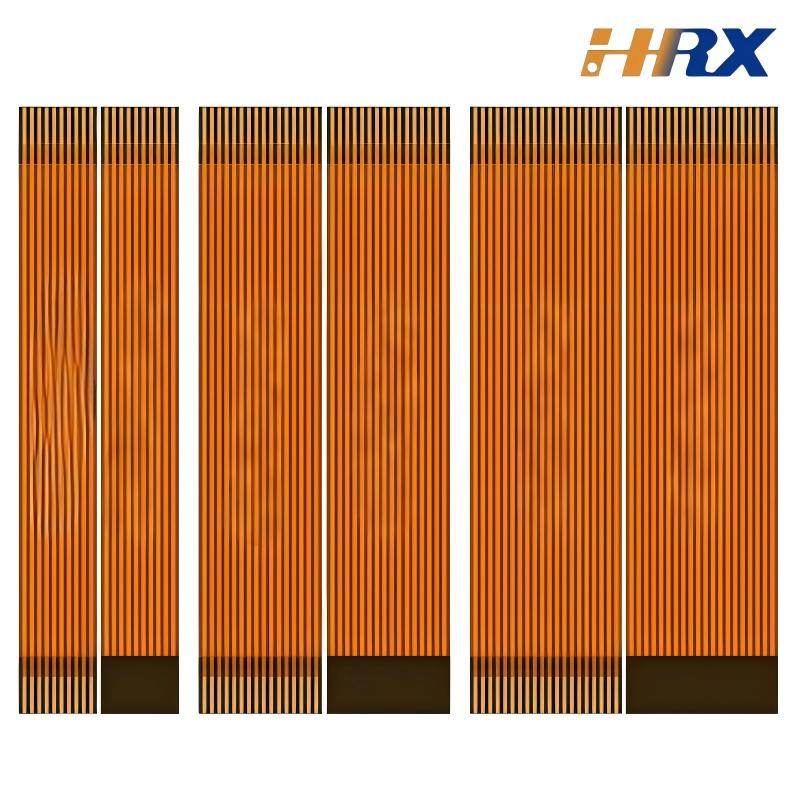
1. Visual Inspection (VI)
Visual inspection is the foundational quality control step, conducted manually or via automated optical inspection (AOI) systems. This process identifies:
Surface defects: Scratches, delamination, solder mask inconsistencies, or misaligned components.
Layer registration: Proper alignment of rigid and flexible layers, critical for FPC-PCB integration.
Routing accuracy: Precise cutouts for flex zones to ensure bendability without mechanical stress.
2. Electrical Testing
Electrical integrity is non-negotiable for rigid-flex boards. Key tests include:
Continuity and Shorts Testing: Uses bed-of-nails fixtures or flying probe systems to verify conductor pathways, ensuring no open circuits or short circuits, especially in complex multilayer flex-rigid designs.
Impedance Testing: Measures characteristic impedance of transmission lines to meet high-frequency requirements (e.g., for RF or high-speed digital signals), critical in aerospace and medical applications.
Dielectric Withstand Voltage Testing: Checks insulation between layers to prevent arcing or leakage, essential for boards with dense circuitry.
Professional tip: Advanced AOI systems with electrical test integration reduce false positives and improve throughput for high-volume production.
3. Mechanical Performance Testing
Rigid-flex boards must withstand repeated bending and mechanical stress. Tests include:
Bend Radius Evaluation: Ensures flex layers meet design specifications for minimum bend radius, preventing copper cracking or dielectric fatigue.
Peel Strength Testing: Measures adhesion between copper traces and flexible substrates (e.g., polyimide or PI films), critical for flexible circuit reliability.
Thermal Cycling Tests: Simulates extreme temperature changes to assess layer stability and material compatibility, reducing risks of delamination in harsh environments.
4. Material and Layer Analysis
In-depth material characterization ensures long-term durability:
Cross-Sectional Microscopy: Examines layer thickness, copper plating uniformity, and adhesive bond quality in rigid-flex interfaces. This is vital for multilayer FPC-PCB bonding and avoiding voids in laminate structures.
FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): Verifies material composition (e.g., PI, FR-4, or adhesives) to confirm compliance with RoHS, REACH, or UL standards.
Surface Roughness Testing: Measures copper surface profile to optimize solderability and reduce signal loss in high-frequency flex segments.
5. Environmental Stress Testing
For applications in extreme environments (e.g., automotive, aerospace), boards must pass:
Humidity and Temperature Testing: Accelerated aging via chambers to evaluate moisture resistance and thermal stability.
Vibration and Drop Testing: Simulates real-world mechanical stress to identify loose components or cracked traces in rigid-flex joints.
Chemical Resistance Testing: Assesses durability against solvents, fluxes, or cleaning agents used in assembly processes.
6. Automated X-Ray Inspection (AXI)
AXI is indispensable for non-destructive evaluation of hidden features:
Layer Alignment Verification: Visualizes internal layer registration in buried vias or blind vias of rigid-flex boards.
Solder Joint Analysis: Detects voids, cold joints, or bridging in BGA (ball grid array) components, critical for reliable interconnections.
Industry trend: 3D X-ray tomography ("micro-CT") is gaining traction for ultra-precise analysis of complex rigid-flex geometries.
7. Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Proactive quality management involves:
Data-Driven Monitoring: Tracking key process parameters (e.g., etching depth, lamination pressure) using SPC charts to identify trends before defects occur.
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process): Formal validation of production capabilities for critical projects, ensuring repeatability in high-reliability rigid-flex manufacturing.
Conclusion: Elevating Rigid-Flex Quality with Holistic QC
At Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics, our commitment to excellence combines advanced inspection technologies with decades of expertise in FPC/PCB/rigid-flex design and manufacturing. By integrating AOI, X-ray, and mechanical testing with material science rigor, we deliver boards that meet the most demanding specifications.
For customized rigid-flex solutions or quality assurance insights, visit www.hrxfpc.com or contact us at sales@hrxfpc.com. Let’s collaborate to engineer reliable, high-performance interconnects for your next project.

Let’s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!
-
 Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly.
Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly. - WHAT WE DO — PCB Design Solutions — Flex PCB Production — Components Sourcing — FPC&PCB Assembly
- PRODUCTS — Single Sided Flexible Circuits — Double Sided Flexible Circuits — Multilayer Flexible Cirucits — Rigid-Flex Circuits — FPC Assembly — PCB Assembly
- CAPABILITY — FPC Capability — Rigid-Flex Capability — PCB Capability — Assembly Capability
- Copyright © 2024 Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
- Design By BONTOP