Search
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rigid and Flex Printed Boards: A Comprehensive Guide for Electronics Professionals
- Jun 11,2025
-
Share
In the highly competitive arena of electronics manufacturing, Rigid Printed Boards (Rigid PCBs) and Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) are two cornerstone technologies, each boasting unique advantages and presenting specific challenges. As a leading global ODM/OEM manufacturer specializing in FPC, PCB, and Rigid-Flex Printed Boards, Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. has in - depth expertise in leveraging these technologies to deliver customized solutions.
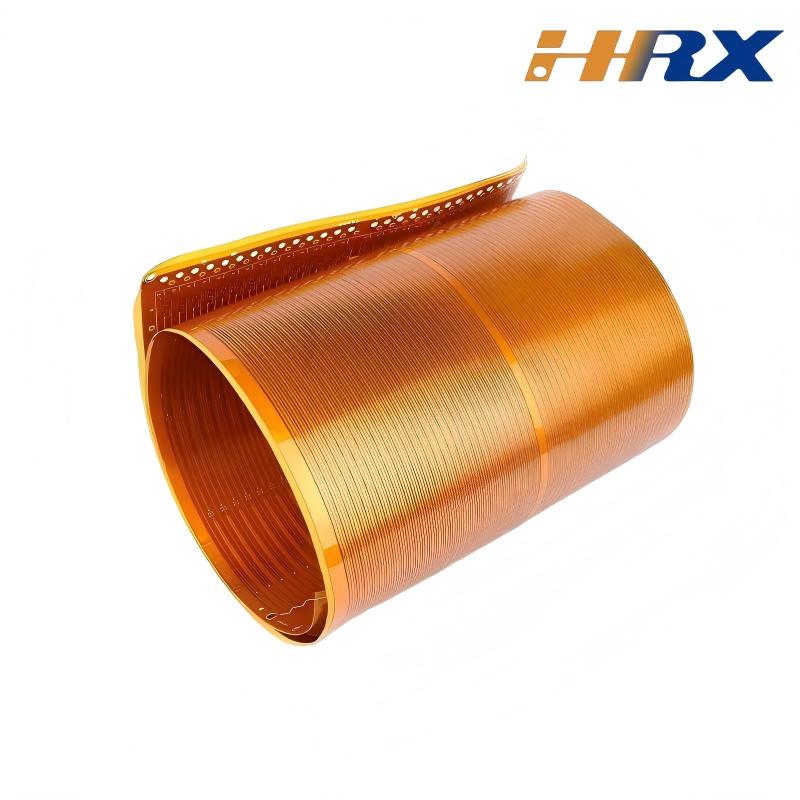
Advantages of Rigid Printed Boards
Structural Stability
One of the most prominent advantages of Rigid PCBs lies in their outstanding structural stability. Fabricated from materials like fiberglass - reinforced epoxy (FR - 4), these boards offer a robust framework that effectively supports and safeguards electronic components. The rigidity ensures that components remain firmly in place during the entire lifecycle, from assembly and operation to transportation, significantly reducing the risk of mechanical damage. In applications such as server farms and high - performance desktop computers, where precise component alignment and secure mounting are paramount, Rigid PCBs are the go - to choice. Their robustness guarantees long - term reliable performance, minimizing the occurrence of component displacement or connection failures. The consistent and stable structure also contributes to the overall reliability of the electronic system, making Rigid PCBs a preferred option for industries where stability is non - negotiable.
Ease of Assembly
Rigid PCBs are renowned for their assembly - friendly nature, which translates into cost - effectiveness and shorter production cycles. Thanks to standardized manufacturing processes and well - defined assembly techniques, component mounting using surface - mount technology (SMT) or through - hole technology (THT) is a relatively straightforward process. Automated assembly equipment can be seamlessly integrated into the production line for Rigid PCBs, significantly increasing production speed while reducing human - induced errors. For instance, in the mass production of consumer electronics like wireless routers and gaming consoles, the ease of assembly of Rigid PCBs enables manufacturers to rapidly scale up production to meet market demands. This advantage not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also helps in controlling production costs, making Rigid PCBs an attractive option for high - volume production scenarios.
Electrical Performance
Rigid PCBs typically exhibit excellent electrical performance. The rigid substrate provides a consistent dielectric constant, which is essential for stable signal transmission and effective reduction of electromagnetic interference (EMI). With the ability to support multi - layer circuit designs, Rigid PCBs can accommodate a large number of components in a compact space, enabling complex circuit integrations. In high - performance computing applications, where high - speed data transfer and precise signal integrity are critical, the reliable electrical properties of Rigid PCBs ensure optimal system operation. The stable electrical environment offered by Rigid PCBs makes them suitable for applications that demand high - precision signal processing, such as data centers and advanced computing systems.
Disadvantages of Rigid Printed Boards
Limited Flexibility
The inherent rigidity of Rigid PCBs severely restricts their application in scenarios that require flexibility or movement. They are ill - suited for applications where the circuit needs to bend, fold, or conform to irregular shapes. For example, in the burgeoning fields of wearable electronics and medical implants, where devices need to adapt to the contours of the human body, Rigid PCBs cannot meet the form - factor requirements. This limitation has led to the emergence of alternative technologies like FPCs in these innovative and rapidly growing industries. The lack of flexibility in Rigid PCBs can also pose challenges in applications where space is at a premium and components need to be arranged in a more dynamic manner, limiting their use in certain cutting - edge electronic designs.
Bulky and Heavy
Compared to FPCs, Rigid PCBs are generally bulkier and heavier due to their thick and rigid structure. This characteristic can be a significant drawback in applications where space and weight are critical factors, such as aerospace and portable electronics. The added weight and size not only impact the overall design aesthetics but can also have practical implications, such as reducing battery life or limiting the available space for other components. In aerospace applications, where every gram of weight can affect fuel consumption and performance, the bulkiness of Rigid PCBs may necessitate the use of alternative, lighter - weight circuit solutions. Similarly, in portable devices like smartphones and tablets, the space occupied by Rigid PCBs can limit the design flexibility and potentially reduce the capacity of batteries or other essential components.
Advantages of Flexible Printed Circuits
Flexibility and Form - Factor
The defining feature of FPCs is their unparalleled flexibility. Constructed from materials such as polyimide or polyester films, FPCs can endure bending, folding, and twisting without sacrificing electrical performance. This flexibility enables the creation of compact, three - dimensional circuit designs that can conform to complex shapes and spaces. In automotive electronics, FPCs are widely used to route signals in tight spaces within the engine compartment or to connect components in the dashboard, where traditional Rigid PCBs would be too large and inflexible. In consumer electronics, the flexibility of FPCs has paved the way for innovative designs, such as foldable smartphones. The ability to adapt to various form - factors allows designers to create more ergonomic and space - efficient products, enhancing the user experience. FPCs can also incorporate features like Coverlay, a thin polyimide film with Adhesive Backing, which provides protection to the copper traces while maintaining flexibility.
Space - Saving
FPCs offer significant space - saving benefits by enabling circuit routing in multiple planes. This eliminates the need for additional connectors and cables that are typically required with Rigid PCBs, resulting in a substantial reduction in space consumption. This makes FPCs highly suitable for miniaturized electronic devices, where every millimeter of space is precious. In medical devices like endoscopes, FPCs play a crucial role in integrating complex circuits within a very small footprint, enhancing the device's functionality while maintaining its compact size. The space - saving nature of FPCs also allows for more efficient use of the available space within electronic enclosures, enabling the integration of additional components or features without increasing the overall size of the device.
Durability in Dynamic Environments
FPCs are engineered to withstand repeated bending and flexing, making them the ideal choice for applications subject to movement, vibration, or mechanical stress. In robotics, where components are constantly in motion, FPCs can maintain reliable electrical connections over extended periods. Their durability in dynamic environments ensures the long - term performance and reliability of the electronic systems they are part of. The ability of FPCs to endure mechanical stress without failure is a result of their specialized construction and material properties. For example, the use of high - quality polyimide films with excellent fatigue resistance and proper trace routing techniques contribute to the overall durability of FPCs in challenging environments.
Disadvantages of Flexible Printed Circuits
Higher Manufacturing Costs
The manufacturing process of FPCs is significantly more complex and time - consuming compared to that of Rigid PCBs. Specialized equipment and advanced techniques, such as laser drilling for vias and precise lamination processes, are required to produce FPCs, which substantially increases production costs. Additionally, the use of high - quality flexible materials, such as polyimide, further adds to the overall expense. This higher cost can be a major deterrent for applications with strict budget constraints, especially in mass - market consumer products where cost - effectiveness is a top priority. The complex manufacturing process also requires more skilled labor and tighter quality control measures, which contribute to the overall cost of FPC production.
Assembly Challenges
Assembling components on FPCs presents unique challenges due to the flexible nature of the substrate. The delicate FPCs are more prone to damage during handling, soldering, and component placement compared to Rigid PCBs. Specialized assembly processes and highly skilled operators are often necessary to ensure proper component attachment and reliable electrical connections. This can lead to longer assembly times and potentially higher defect rates if not managed carefully. For example, the use of vacuum - assisted handling techniques and precise soldering equipment is essential to prevent damage to the FPC during assembly. The need for specialized assembly methods and skilled labor adds to the overall cost and complexity of using FPCs in electronic products.
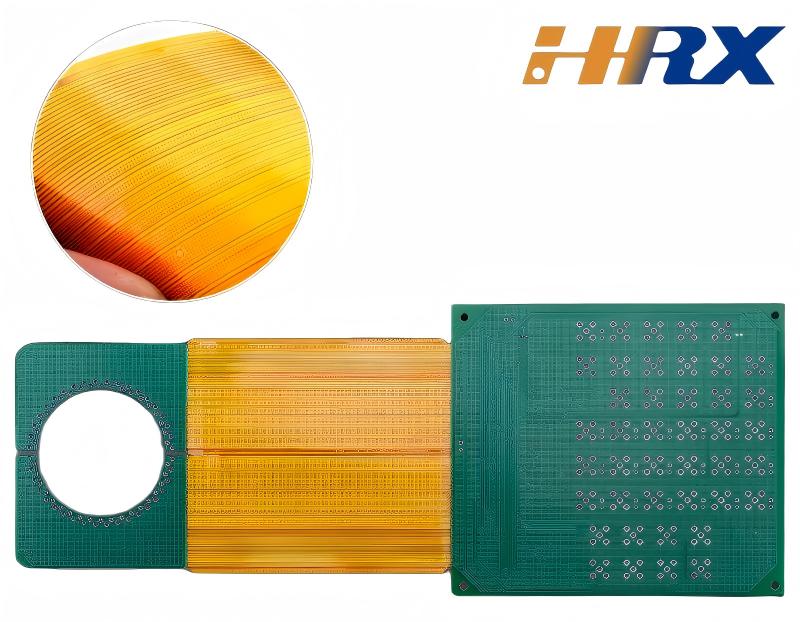
In conclusion, both Rigid PCBs and FPCs have their own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the electronic application, including mechanical constraints, electrical performance needs, space limitations, and cost considerations. At Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd., our expertise in both Rigid PCB Assembly and Flexible Printed Circuit Manufacturing allows us to provide customized solutions that meet the diverse needs of our clients. Whether you require the stability of Rigid PCBs, the flexibility of FPCs, or a combination of both in the form of Rigid - Flex Printed Boards, we are well - positioned to assist. Visit our website www.hrxfpc.com or email us at sales@hrxfpc.com to explore how we can support your next electronics project and leverage our industry - leading capabilities in PCB and FPC technologies.

Let’s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!
-
 Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly.
Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly. - WHAT WE DO — PCB Design Solutions — Flex PCB Production — Components Sourcing — FPC&PCB Assembly
- PRODUCTS — Single Sided Flexible Circuits — Double Sided Flexible Circuits — Multilayer Flexible Cirucits — Rigid-Flex Circuits — FPC Assembly — PCB Assembly
- CAPABILITY — FPC Capability — Rigid-Flex Capability — PCB Capability — Assembly Capability
- Copyright © 2024 Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
- Design By BONTOP